Sound in rooms
The surroundings influence acoustics
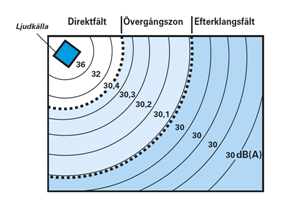
Acoustics are influenced by the interiors of a room or space. The placement of the acoustic source and the device for measuring noise affects the sound pressure. Sound sources placed against walls or in corners increase the noise level in a space. The sound pressure decreases with distance from the source.

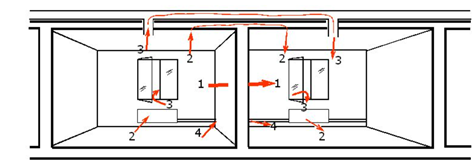
Sound transmission paths
Sound can be transmitted in different ways. Direct sound propagates in the air directly to the human body without bouncing against walls and ceilings. Reflective sound is any sound that bounces off walls, floors and ceilings before reaching the human ear. Vibrating sound, e.g. transmission noise and structure-borne noise, is transmitted to our ears via rigid matter such as walls, floors and ceilings.
- Direct sound transmission
- Flank transmission
- Cross-talk
- Leakage

Attenuation using carpets and curtains
A room's ability to absorb sound is described as its equivalent sound absorption area. A value is obtained by multiplying each surface' area by the absorption factor of each surface, the latter being the ratio of reverberated sound to incident sound. We can lower the noise level in a room by introducing materials like floor mats, curtains and cushioned furniture.